10~11세 사춘기 아이들의 성장 발육, Growth and development of 10 ~11 year old adolescents
표 3-57. 10세 사춘기 아이들의 체중과 신장의 백분위수
|
백분위수 성별 |
3 | 10 | 25 | 50 | 75 | 90 | 97 | |
| 남아 | 체중(kg) | 22.00 | 23.40 | 25.00 | 27.00 | 29.30 | 31.50 | 35.00 |
| 신장(cm) | 121.7 | 124.5 | 128.0 | 131.9 | 135.5 | 139.3 | 143.0 | |
| 여아 | 체중(kg) | 21.20 | 23.00 | 24.50 | 26.50 | 29.00 | 31.50 | 35.00 |
| 신장(cm) | 121.1 | 124.4 | 127.7 | 131.6 | 135.3 | 139.7 | 143.7 |
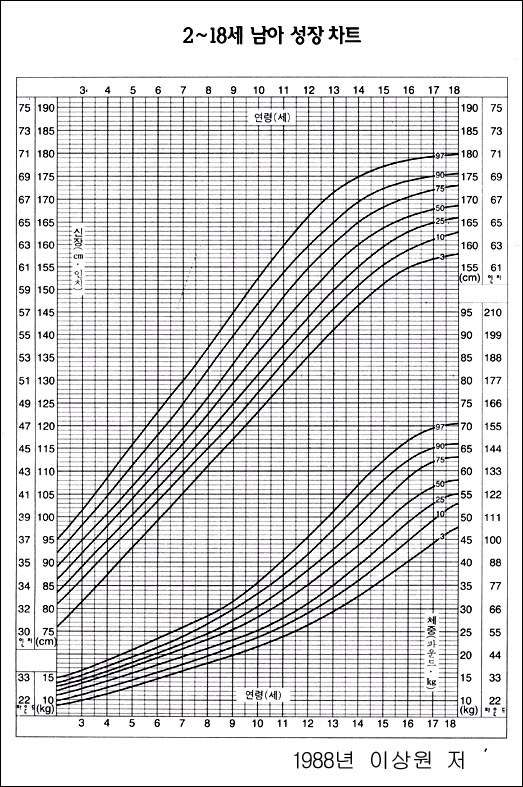
그림 3-270. 2~18세 한국 남아들의 체중과 신장의 성장차트와 백분위수
Copyright ⓒ 2011 John Sangwon Lee, MD., FAAP
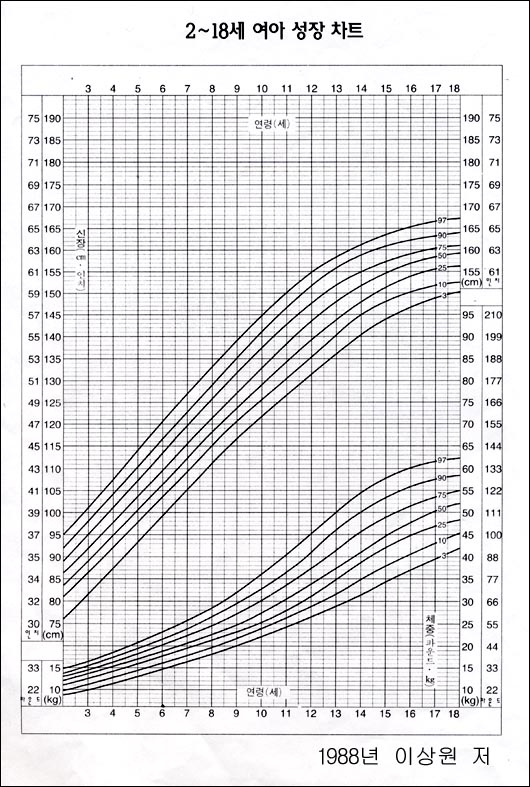
그림 3-271. 2~18세 한국 여아들의 체중과 신장의 성장차트와 백분위수
Copyright ⓒ 2011 John Sangwon Lee, MD., FAAP
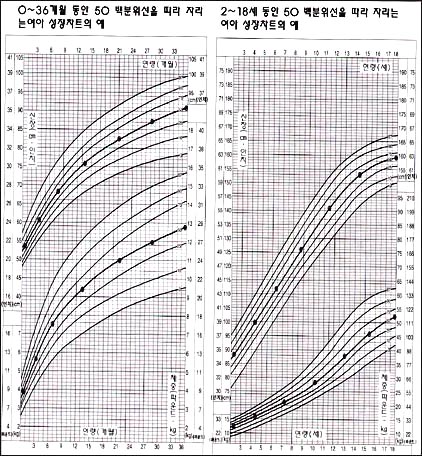
그림 3-272. 0~18세 체중과 신장의 성장차트
50 백분위선을 따라 성장하는 여아의 성장차트의 예
Copyright ⓒ 2011 John Sangwon Lee, MD., FAAP
- 사춘기 아이의 체중과 신장을 잰다.
- 잰 체중 치와 신장 치를 성장차트 체중·신장 백분위선에 그려 넣고 체중과 신장이 성장차트 백분위선 상 어디에 있는지 알아본다.
- 그 사춘기 아이의 체중과 신장이 전과 거의 같은 성장차트 체중·신장 백분위선을 따라 계속 증가되면서 정상적으로 잘 자라나 알아본다.
- 이 나이의 초기 사춘기 아이들은 남녀 성별, 환경, 인종, 타고난 체질, 영양 등에 따라 성장 발육의 속도에 차이가 크다.
- 사춘기가 시작하는 남녀아의 나이 차이 때문에 같은 나이의 초기 사춘기 여아들과 초기 사춘기 남아들의 성장과 발육에 차이가 많이 날 수 있다.
- 여아들의 사춘기는 남아들의 사춘기 보다 1~2년 더 일찍 오는 것이 보통이다.
- 그 때문에 사춘기가 온 초기 사춘기 여아들의 신장이 아직 사춘기가 오지 않은 또래 남아들의 신장보다 더 클 수 있다.
소아의 나이에 따른 추정 체중치
- 한국 만삭 남 신생아 출생 시 평균 체중은 3.3~3.4Kg이고 만삭 여 신생아 출생 시 평균체중은
- 3.24kg 이다 6.
- 만삭에 태어난 신생아들이 출생 이후 정상적으로 감소됐던 체중은 생후 10일 경까지 증가돼서 출생 시 체중으로 된다.
- 만삭에 태어난 대부분의 영아들의 생후 5개월 체중은 출생 시 체중의 배가된다.
- 만삭에 태어난 대부분의 영아들의 1세 체중은 출생 시 체중의 3배가된다.
- 생후 10일에서 생후 5~6개월까지 매일 20~30gm 정도 체중이 증가된다.
- 생후 6~12개월 동안 매일 10~20gm 정도 체중이 증가된다.
- 3세 체중은 출생 시 체중의 4배정도 된다.
- 5세 체중은 출생 시 체중의 5배정도 된다.
- 7세 체중은 출생 시 체중의 7배정도 된다.
- 10세 체중은 출생 시 체중의 10배정도 된다.
- 15세 체중은 출생 시 체중의 15배정도 된다.
생후 3개월부터 12세 소아들의 추정 체중치 계산 공식
- 3~12개월 영아의 체중(kg) = [나이(월령) + 9]/2
- 1~6세 유아의 체중(kg) = 나이(년) x 2 + 8
- 7~12세 아이의 체중(kg) = [나이(년) x 7 -5)]/2
소아의 나이에 따른 추정 신장치
- 건강한 영아들의 신장은 생후 1년 동안 25-30cm 정도 더 자란다.
- 성인 남성의 예측 신장치(cm)는 (엄마의 신장 + 아빠의 신장)/2 + 5cm이고
- 성인 여성의 예측 신장치(cm)는 (엄마의 신장 + 아빠의 신장)/2 – 5cm이고
- 2세 신장치는 그 아이가 성인이 될 때의 신장치의 반이 되고
- 성인 남성 예측 신장치(cm)는 1.27 x 3세의 신장 + 54.9(cm)이고
- 성인 여성 예측 신장치(cm)는 1.29 x 3세의 신장 + 42.3 이다
소아의 나이에 따른 추정 신장치
- 7~12세 아이들의 추정 평균 신장(cm)= 나이(년) x6+77
Growth and development of 10-11-year-old adolescents
Table 3-57. Percentiles of weight and height in 10-year-old adolescents percentile 표 3-57. 10세 사춘기 아이들의 체중과 신장의 백분위수
|
백분위수 성별 percentile Gender |
3 | 10 | 25 | 50 | 75 | 90 | 97 | |
| 남아 Boy | 체중(kg)
weight (kg) |
22.00 | 23.40 | 25.00 | 27.00 | 29.30 | 31.50 | 35.00 |
| 신장(cm)
Height (cm) |
121.7 | 124.5 | 128.0 | 131.9 | 135.5 | 139.3 | 143.0 | |
| 여아 Female | 체중(kg)
weight (kg) |
21.20 | 23.00 | 24.50 | 26.50 | 29.00 | 31.50 | 35.00 |
| 신장(cm)
Height (cm) |
121.1 | 124.4 | 127.7 | 131.6 | 135.3 | 139.7 | 143.7 |

Figure 3-270. Growth charts and percentiles of weight and height for Korean boys aged 2 to 18 years Copyright ⓒ 2011 John Sangwon Lee, MD., FAAP

Figure 3-271. Growth chart and percentiles of weight and height for Korean girls aged 2 to 18 years Copyright ⓒ 2011 John Sangwon Lee, MD., FAAP

Figure 3-272. Growth chart of weight and height from 0 to 18 years old Example of a growth chart for girls growing along the 50th percentile Copyright ⓒ 2011 John Sangwon Lee, MD., FAAP
• Measure the weight and height of the adolescent child.
• Draw the measured weight and height values on the growth chart weight/height percentile line, and find out where your weight and height are on the growth chart percentile line.
• Find out if the adolescent child is growing normally as his weight and height continue to increase along with the weight and height percentiles of the growth chart, almost the same as before.
• Early puberty children at this age have great differences in growth and development rates depending on gender, environment, race, innate constitution, and nutrition.
• Because of the age difference between boys and girls at the onset of puberty, there can be significant differences in growth and development between girls of the same age and boys of early puberty.
• Puberty in girls usually comes one to two years earlier than puberty in boys.
• As a result, early puberty girls who have reached puberty may be taller than boys of their age who have not yet reached puberty.
Estimated weight according to the age of the child
• The average weight at birth of full-term male newborns in Korea is 3.3~3.4Kg, and the average weight at birth of full-term female newborns in Korea is
• It is 3.24 kg 6.
• For full-term newborns, the normal weight loss after birth increases until around the 10th day of life and becomes the birth weight.
• Most infants born full-term weigh at least twice their birth weight at 5 months of age.
• Most infants born to full term weigh at least three times their weight at birth.
• From the 10th day of life to the 5th to 6th month of life, you gain 20-30gm of body weight every day.
• During 6 to 12 months of age, they gain 10-20 gm of body weight every day.
• A 3-year-old weighs four times its birth weight.
• Five-year-olds weigh about five times their birth weight.
• 7-year-olds weigh about 7 times their birth weight.
• A 10-year-old weighs about 10 times her birth weight.
• A 15-year-old weighs about 15 times its birth weight.
Estimated weight calculation formula for children aged 3 months to 12 years
• Weight (kg) of infants 3-12 months = [age (months) + 9]/2
• Weight (kg) of infants aged 1-6 = Age (years) x 2 + 8
• Weight (kg) of children aged 7-12 = [age (years) x 7 -5)]/2
Estimated Kidney Device by Child’s Age
• Healthy infants grow an extra 25-30 cm during the first year of life.
• The predicted height of an adult male (cm) is (Mother’s height + Dad’s height)/2 + 5 cm.
• The predicted height of an adult woman (cm) is (mother’s height + dad’s height)/2 – 5 cm. • A 2-year-old’s height will be half that of the child’s adult.
• The predicted height for an adult male (cm) is 1.27 x 3 years old + 54.9 (cm).
• The estimated height of an adult female (cm) is 1.29 x 3 years old + 42.3
Estimated Kidney Device by Child’s Age
• Estimated average height (cm) of children aged 7-12 = age (years) x6+77
출처 및 참조 문헌 Sources and references
- NelsonTextbook of Pediatrics 22ND Ed
- The Harriet Lane Handbook 22ND Ed
- Growth and development of the children
- Red Book 32nd Ed 2021-2024
- Neonatal Resuscitation, American Academy of Pediatrics
- The Johns Hopkins Hospital, The Harriet Lane Handbook, 22nd edition
- Red book 31st edition 2021
- Nelson Text Book of Pediatrics 21st Edition
- Infectious disease of children, Saul Krugman, Samuel L Katz, Ann A. Gershon, Catherine Wilfert
- Emergency Care Transportation of Sick and Injured American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons
- Emergency Pediatrics A Guide to Ambulatory Care, Roger M. Barkin, Peter Rosen
- Gray’s Anatomy
- Ambulatory Pediatrics, Green and Haggerty, Saunders
- Introduction to Clinical Pediatrics, Smith and Marshall, W.B. Saunders Co
- School Health: A Guide For Health Professionals, American Academy of Pediatrics
- Holly Bible
- How to really love your child Ross Campbell
- Good Behavior Stephen W. Garber, Ph.D. and other
- Kids Who follow, Kids who don’t
- Loving Each Other Leo F Buscaglia, Ph, D.
- Guide to Your Child’s Sleep. American Academy of Pediatrics
- Hematology and Oncology in Adolescence, Neil J. Grossman, M.D., Stuart S. Winter, M.D., Adolescent Medicine, and The Media Adolescents Medicine
- AM: Stars Adolescent Medicine: State of the Art Reviews, Asthma, and Diabetes in Adolescents, Robert A. Wood, M.D., Samuel J. Casella, M.D. April 2010, AAP
- AM: Stars Adolescent Medicine: State of the Art Reviews, Sleep and Sleep Disorders in Adolescents, Amy E. Sass, M.D., MPH, David W. Kaplan, M.D., MPH Editors December 2010, AAP
- The Pediatric Clinics of North America, Adolescent Gynecology, Part II THe Sexually Active Adolescent, August 1999
- The Pediatric Clinics of North America, Childhood and Adolescent Obesity, August 2001
- Adolescent Dermatology, Daniel P. Krowchuk, M.D., Anne W. Lucky, M.D., Adolescent Medicine, 12:2 June 2001
- Gastrointestinal Disorders, Jeffrey S. Hyams. M.D. Editor, Adolescent Medicine
- Fueling the Teen Machine, Ellen Shanley and Colleen Thompson
- Why Teenagers Act the Way They Do, Eight Adolescent Personality Types: Understanding and Dealing With Them, Dr. G. Keith Olson
- Adolescent Psychiatry, Adolescent Medicine Clinics, Feb. 2006 Vol 17 #1 Richard E. Kreipe, M.D., Christopher H. Hodgman, M.D.
- Adolescent and the Media, Adolescent Medicine Clinics June 2005 Vol 16 #3, Guest Editors: Victor C. Strasburger, Marjorie J. Hogan, M.D.
- 진정한 자녀 사랑 나비게이터
- 10대 아들 딸 이렇게 사랑해 키워라 이상원 역저 (How to really love your teenager. Ross Campbell MD)
- 소아과학 대한교과서
- 의학 용어사전 대한 의사 협회
- 그 외
Copyright ⓒ 2014 John Sangwon Lee, MD., FAAP
“부모도 반의사가 되어야 한다”-내용은 여러분들의 의사로부터 얻은 정보와 진료를 대신할 수 없습니다.
“The information contained in this publication should not be used as a substitute for the medical care and advice of your doctor. There may be variations in treatment that your doctor may recommend based on individual facts and circumstances.
“Parental education is the best medicine.